Clostridium difficile is a bacterium that normally resides without causing any problem in the gut of approximately 5% of the population1. Following antibiotic treatment, the bacterial colonization in the intestine decreases which promotes the proliferation of C. difficile and thereby the infection by the bacteria. Well entrenched the bacteria produce toxins that can damage the gut and cause diarrhea2. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) is the leading cause of nosocomial diarrhea3.
Most people with the disease recover with antibiotic treatment, although researchers estimate that more than 20% of patients with C. difficile infection fail initial treatment4. Moreover, some more vulnerable patients may have serious complications such as severe bowel inflammation or severe dehydration2.
It is also possible to find blood, mucus or pus in the stools.
People taking antibiotics are 7 to 10 times more likely to have the infection5. People in hospitals or nursing homes are also more at risk6.
Montreal-based Santa Cabrini Hospital administered Probaclac Adult probiotics to all patients who received antibiotic treatment to control the spread of the infection.
Conducted over a period of 8 months with 5000 people, the double-blind study was completely independent of Laboratoires Nicar.
The CDAD decreased in patients at the hospital.
The administration of Probaclac probiotics as a preventative measure to avoid the spread of C. difficile infections has been effective7.
Important risk reduction in nosocomial clostridium difficile with institution of probiotic prophylaxis - abstract
Download the studyImportant risk reduction in nosocomial clostridium difficile with institution of probiotic prophylaxis - full study
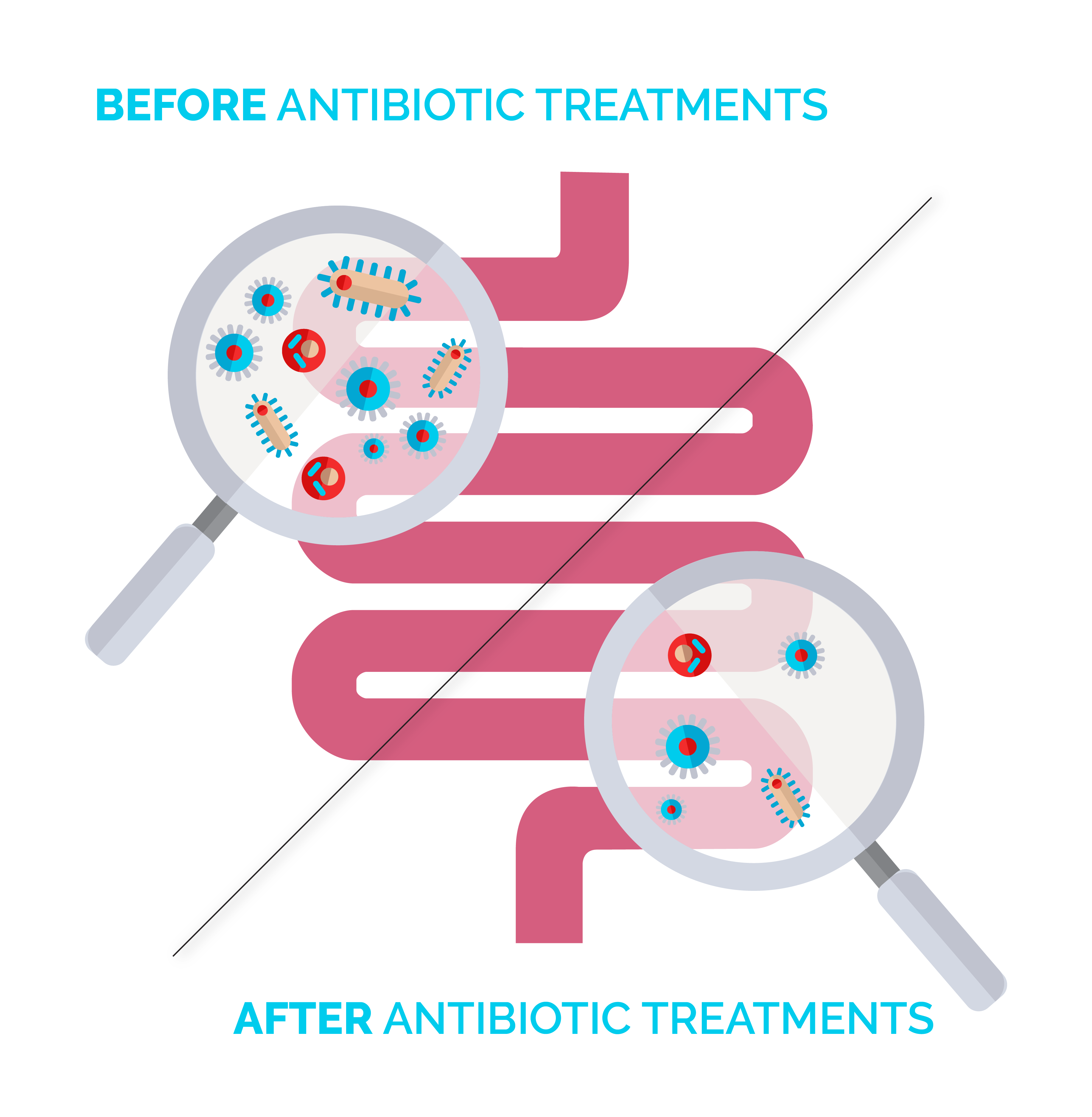
Download the studyBroad-spectrum antibiotics work against a large number of bacteria to fight infections.
They are an effective weapon to handle with caution as they attack bacteria without distinguishing between pathogenic bacteria responsible for infection and good bacteria of the intestinal flora. They are the perfect example of a double-edged medical sword8.
The resulting intestinal bacterial imbalance can lead to antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD).
Several studies have confirmed the efficacy of the probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii, also known as S. boulardii, in the preventive treatment of this unfortunate consequence of antibiotic therapy.
This probiotic can not be affected by antibiotics and helps restore the intestinal flora to avoid unpleasant intestinal disturbances9.
A randomized, double-blind study of 151 hospitalized adult patients demonstrated the efficacy of the probiotic.
The placebo group developed diarrhea in a ratio of 9% while the supplemented group had a ratio of 1.4%, a 7.6% decrease10.
The beneficial effect of the probiotic was also replicated in a double-blind randomized controlled trial in 269 children aged 6 months to 14 years11.
The Probaclac Medic formula contains 5 billion active cells per capsule, the same amount as that administered to the experimental group in the study in the adult population.
Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in children: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
Download the studyProphylactic Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: A prospective study
Download the studyThe effect of oral administration of Lactobacillus GG on antibiotic- associated gastrointestinal side-effects during Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy
Download the studyEffect of Different Probiotic Preparations on Anti–Helicobacter pylori Therapy–Related Side Effects: A Parallel Group, Triple Blind, Placebo- Controlled Study
Download the studyEffect of Lactobacillus GG Supplementation on Antibiotic-Associated Gastrointestinal Side Effects during Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy: A Pilot Study
Download the studyThe vaginal flora is composed of microorganisms, including a very large quantity of lactobacilli bacteria, called the Döderlein flora, which represents approximately 95% of the vaginal ecosystem12.
Döderlein's good bacteria form a protective biofilm on the vaginal mucosa13.
The protective effect of lactobacilli is declined in different mechanism of action. Among other things, they inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria by secreting a variety of substances and impair their adhesion to vaginal epithelial cells by filling the surface14.
Although the Döderlein flora is a suitable protection, it is not foolproof and it is possible that an imbalance of the vaginal microbiota occurs.
The balance can be disturbed with a decrease in good bacteria, a proliferation of bad bacteria or yeasts13.
Bacterial vaginosis is a disequilibrium that can be caused by the proliferation of a number of bacteria, including Gardnerella vaginalis or Prevotella, which are normally found in the sub-dominant vaginal flora14.
This change in the ecosystem involves an increase of the normally acidic vaginal pH and thus an infection. This infection is asymptomatic in half of women, however, when symptoms occur they are particularly bothersome for the affected woman16. Typically, they are characterized by heavy vaginal discharge of a gray/greenish smelly substance17.
The effectiveness of Probaclac vaginal probiotics in reducing the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis has been scientifically proven.
The formula contains 8 billion bacteria of 3 different strains and helps to regulate the Döderlein flora by repopulating it.
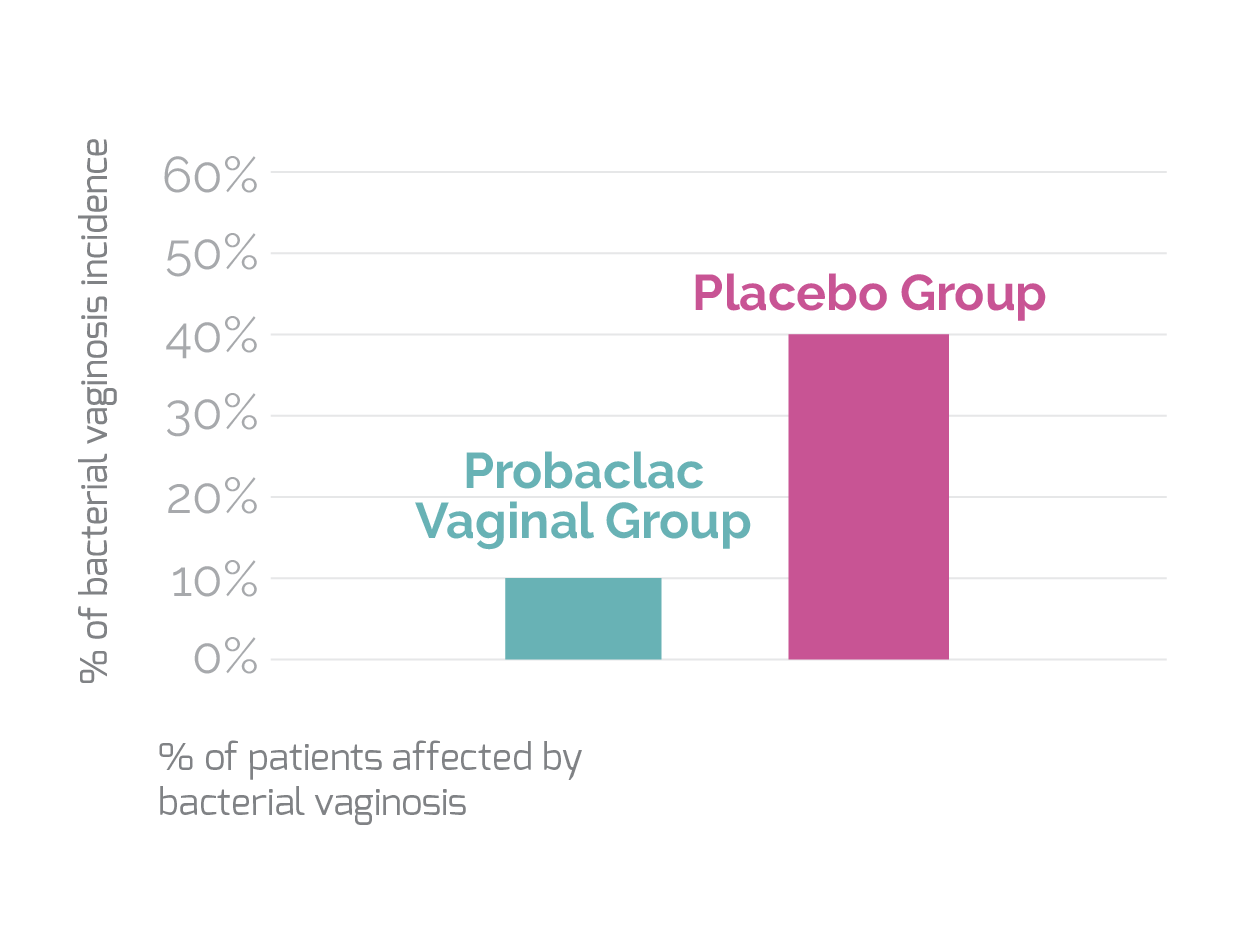
A study was conducted among 120 women with a history of recurrent bacterial vaginosis.
The results are conclusive and demonstrate that the insertion of probiotics into the vaginal cavity reduces the recurrence of bacterial vaginosis by more than 80%18.
Significant reduction of bacterial vaginosis rate over 2 months
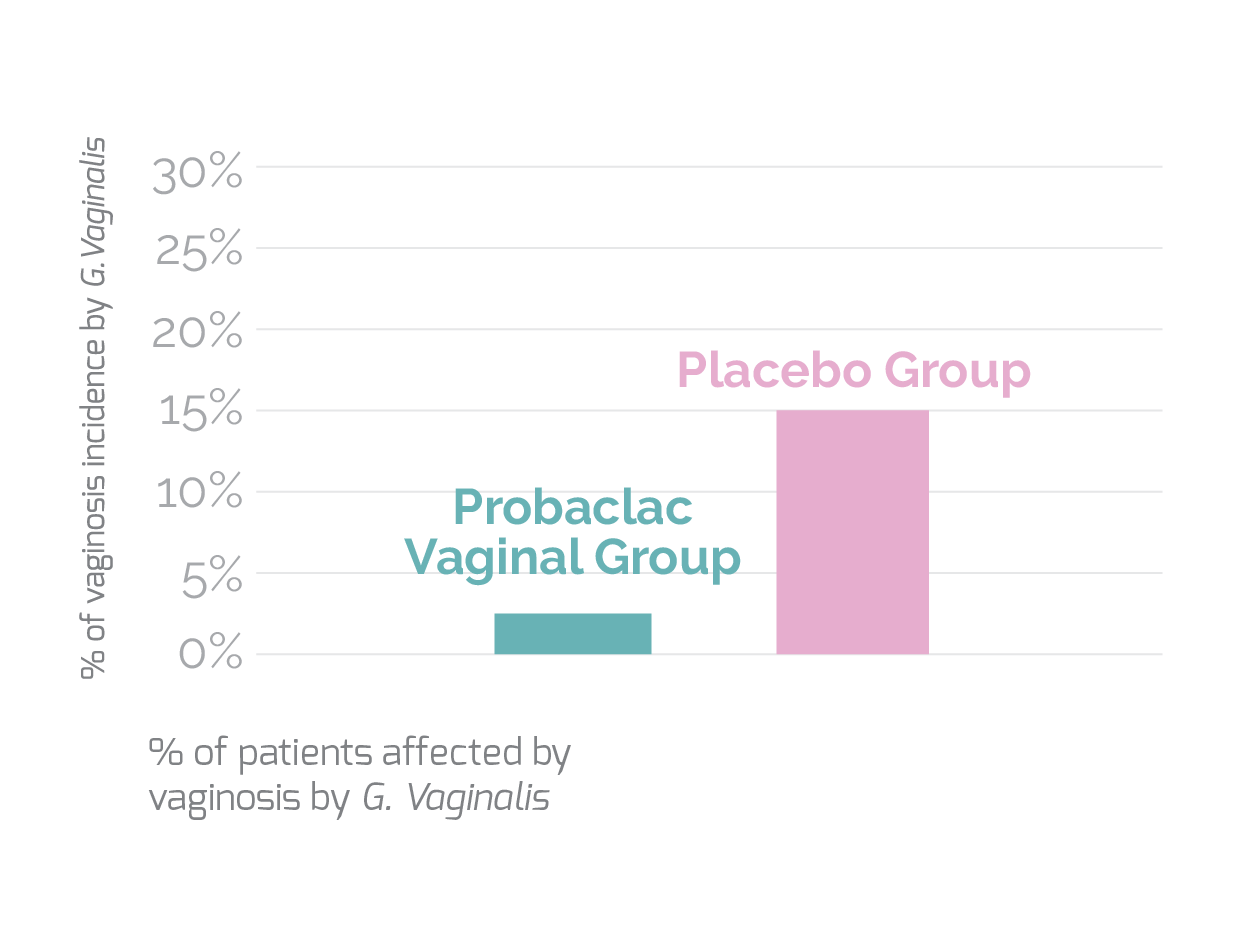
Significant reduction of bacterial vaginosis rate by G. Vaginalis over 2 months
Efficacy of vaginal probiotic capsules for recurrent bacterial vaginosis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study
Download the studyInfectious diarrhea is an acute diarrhea. The WHO defines it by the emission of at least 3 or more loose or liquid stools per day in a time period of less than 2 weeks. The culprits behind the disease are from three different categories: viruses, bacteria or parasites.
Studies suggest that an upset intestinal balance can be restored through probiotic supplementation and rehydration
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is a documented probiotic strain that has demonstrated many benefits for digestive and immune health in many clinical studies.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG clinically demonstrated its propensity to promote the growth of friendly bacteria, which are necessary to maintain the healthy balance of the intestinal flora.3-10
The GG strain has the natural ability to survive gastric acidity and the ability to work as a barrier against the development of intestinal pathogenic bacteria.1-2
Clinical evidence on GG has, among other things, proven its ability to reduce the incidence and duration of diarrhea episodes caused by viral or bacterial infections4-5.
Oral Bacterial Therapy Reduces the Duration of Symptoms and of Viral Excretion in Children with Mild Diarrhea
Download the studyProbiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations
Download the study
1- Gogineni VK, Lee E Morrow and Mark,A.Malesker.
Probiotics: Mechanisms of action and clinical application. Journal of Probiotics & Health. 2013(1):1-11.
2- Segers ME, Lebeer S.
Towards a better understanding of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG - host interactions. Microbial Cell Factories. 2014;13(Suppl 1):S7-S23.
3- Davidson LE, Fiorino AM, Snydman DR, Hibberd PL.
Lactobacillus GG as an immune adjuvant for live-attenuated influenza vaccine in healthy adults: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2011;65(4):501-507.
4- Siitonen S, Vapaatalo H, Salminen S, et al.
Effect of Lactobacillus GG yoghurt in prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhoea. Ann Med. 1990;22(1):57-59.
5- Vanderhoof JA, Whitney DB, Antonson DL, et al.
Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children. J Pediatr. 1999;135:564-568.
6- Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Poussa T, Arvilommi H, Isolauri E.
Probiotics during the first 7 years of life: a cumulative risk reduction of eczema in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(4):1019-1021.
7- Berni Canani R, Nocerino R, Terrin G, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus GG on tolerance acquisition in infants with cow's milk allergy: a randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(2):580-602.
8- Salminen MK, Tynkkynen S, Rautelin H, et al.
Lactobacillus bacteremia during a rapid increase in probiotic use of lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in finland. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35(10):1155-1160.
9- Luoto R, Laitinen K, Nermes M, Isolauri E. Impact of maternal probiotic-supplemented dietary counselling on pregnancy outcome and prenatal and postnatal growth: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(12):1792-1799.
10- Salminen MK, Tynkkynen S, Rautelin H, et al. The efficacy and safety of probiotic lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on prolonged, noninfectious diarrhea in HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy: A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study. HIV Clin Trials. 2004;5(4):183-191.
11- Hilton E, Kolakowski P, Singer C, Smith M. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG as a diarrheal preventive in travelers. J Travel Med. 1997;4(1):41-43.
12- Oksanen PJ, Salminen S, Saxelin M, et al.
Prevention of Travellers’ diarrhoea by lactobacillus GG. Ann Med. 1990;22(1):53-56.
13- Armuzzi A, Cremonini F, Ojetti V, et al.
Effect of lactobacillus GG supplementation on antibiotic-associated gastrointestinal side effects during helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: A pilot study. Digestion.2001;63(1):1-7.
14- Armuzzi A, Cremonini F, Bartolozzi F, et al.
The effect of oral administration of lactobacillus GG on antibiotic-associated gastrointestinal side-effects during helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15(2):163-169.
15- Cremonini F, Di Caro S, Covino M, et al.
Effect of different probiotic preparations on anti-helicobacter pylori therapy-related side effects: A parallel group, triple blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(11):2744-2749.
16- Cremonini F, Di Caro S, Santarelli L, et al.
Probiotics in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Dig Liver Dis. 2002;34(SUPPL. 2):S78-S80.
17- Siitonen S, Vapaatalo H, Salminen S, et al.
Effect of Lactobacillus GG yoghurt in prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhoea. Ann Med. 1990;22(1):57-59.
18- Videlock EJ, Cremonini F. Meta-analysis: Probiotics in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;35(12):1355-1369.
19- Rodgers B, Kirley K, Mounsey A. PURLs: Prescribing an antibiotic? pair it with probiotics. J Fam Pract. 2013;62(3):148-150.
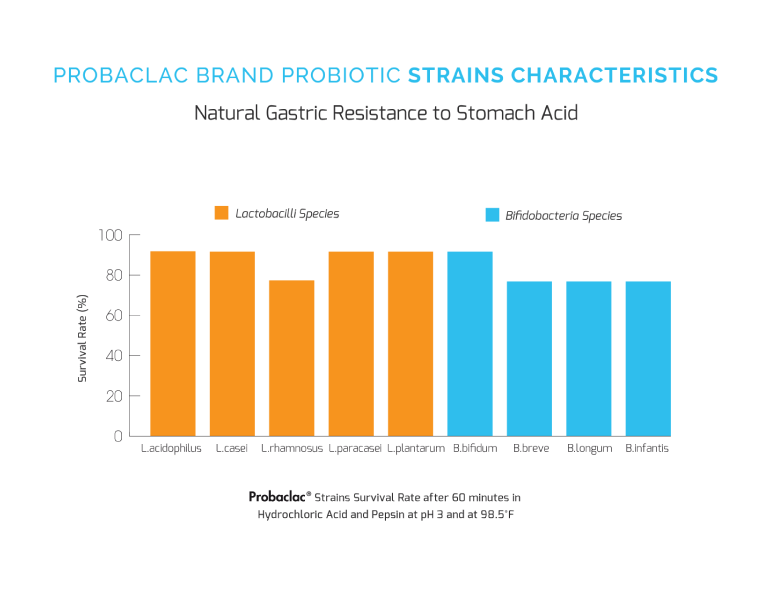
Probaclac probiotic strains survive without an enteric-coated capsule in a pH of 3
Once consumed probiotics follow the natural path through the digestive tract. Starting in the mouth then traveling through the esophagus probiotics then reach the stomach, a very acidic environment when it is empty. Its acidity level varies according to what it contains, in the fasting stomach the pH is at around 1 and it rises to 6 when it is full.
The alkalization of the stomach when it contains nutrients is the reason why it is better to consume probiotics while eating. The number of active bacteria in the supplements can be affected if it faces a very acidic environment.
In order to ensure product efficacy, probiotic manufacturers must be able to demonstrate that their probiotic strains can withstand a pH3 environment. All strains of Probaclac supplements are able to survive an acid trip and therefore the viability of the bacteria is ensured to the intestines. An enteric-coated capsule is not needed for the bacteria to arrive safely. Not to mention that Lactobacillus strains are normally found in the stomach, the path traveled presents an opportunity to repopulate this flora.
1- Santé et services sociaux Québec [Online].
Consulted February 9th 2018.
http://www.msss.-gouv.qc.ca/sujets/prob_sante/nosocomiales/index.php?1-Quest-ce-que-le-Clostridium-difficile
2- Hôpital communautaire de Cornwall [Online].
Consulted February 9th 2018.
https://www.-cornwallhospital.ca/fr/CDFAQFR
3- North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. L’infection à la bactérie Clostridium difficile, la colite causée par le Clostridium difficile ou les diarrhées associées au Clostridium difficile [En ligne].
Novembre 2013. Consulted February 9th 2018.
A high-dose preparation of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in the prevention of antibiotic-associated and Clostridium difficile diarrhoea in older people admitted to hospital: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel arm trial (PLACIDE). Health Technol Assess. 2013 Dec ; 17(57) : 1-140.
https://www.gikids.org/files/documents/digestive%20topics/Clostridium%20difficile%20-%20French%20-%20Final.pdf
4- American Pharmacists Association. Probiotics could prevent C. difficile infections [Online].
February 2018. Consulted February 27th 2018.
http://www.pharmacist.com/article/probiotics-couldprevent-c-difficile-infections
5- Le Journal des Femmes [Online].
février 2018, Consulted February 9th 2018.
http://santemedecine.journaldesfemmes.com/faq/32621-clostridium-difficile-symptomes-et-traitements
6- Centers for disease control and prevention. New CDC Study and Blog: National Burden of Clostridium difficile Infections [Online].
Consulted February 9th 2018.
https://content.govdelivery.com/accounts/USCDC/bulletins/f3c509
7- S Perna, Mlaroche, H Sirvent, K Knowles, S Trifiro, P Lessard, P Barriga. Important risk reduction in Nocosomial Clostridium Difficile with Institution of Probiotic Prophylaxis. Revue canadienne de prévention des infections. Printemps 2006. Bol. 21 No. 1
8- Centre didactiquebiotech [Online].
Consulted February 9th 2018.
http://biotechlerncenter.interpharma.ch/fr/4996-2-comment-agissent-les-antibiotiques
9- RAMBAUD, Jean-Claude, BUTS Jean-Paul, CORTHIER Gérard, FLOURIÉ Bernard, Flore Microbienne intestinale. Physiologie et pathologie digestives. Éditions John Libbey Eurotext, 2004. p.181
10- Mehmet Can, Bulent Ahmet Beşirbellioglu, Ismail Yasar Avci. Can Murat Beker, Alaaddin Pahsa (2006). Prophylactic Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: A prospective study. Department of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey.
11- M. Kotwoswka, P. Albrecht, H. Szajewska (2004). Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in children: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, The Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland.
12- La flore bactérienne vaginale et le pH du vagin [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
http://www.aly-abbara.com/livre_gyn_obs/termes/hygiene/flore_vaginale/flore_vaginale_pH.html
13- Lorraine Evoluence. Qu’est-ce que la flore de Döderlein [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
https://www.lorraine-evoluence.com/sexualite-feminine/flore-de-doderlein/
14- Flore commensale vaginale [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
http://microbiologiemedicale.fr/physiopathologie-et-diagnostic-des-infections/plan-genital/plan-genital-feminin/flore-commensale-vaginale/
15- Mon-gyneco. Flore vaginale normale: la flore de Döderlein. [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
http://www.mon-gyneco.com/florevaginalenormale.html
16- Santé sur le Net. Vaginose bactérienne [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
https://www.sante-sur-le-net.com/sante-femme/gynecologie/vaginose-bacterienne/
17- Passeport santé. Le point sur les différentes infections gynécologiques [Online].
Consulted February 15th 2018.
https://www.passeportsante.net/fr/Actualites/Dossiers/DossierComplexe.aspx?doc=infections-gynecologiques-la-vaginose-bacterienne
18- Ya W, Reifer C, Miller LE. Efficacy of vaginal probiotic capsules for recurrent bacterial vaginosis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo- controlled study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;203:120.e1-6.